Keto Enol Tautomerism: Effective Ways to Understand it in 2025
Understanding Tautomeric Equilibrium in Organic Chemistry
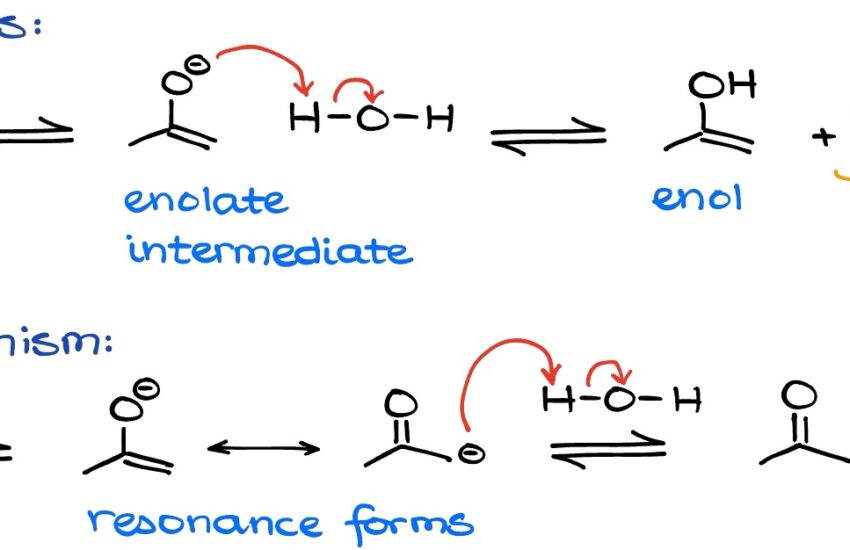
Keto enol tautomerism is a crucial concept in **organic chemistry**, illustrating how certain compounds can exist in two different forms that differ in the arrangement of protons and bonds. The keto form, characterized by a carbonyl group (C=O), transitions to the enol form, which features a hydroxyl group (−OH) bonded to a carbon-carbon double bond. This interconversion is fundamental to understanding **functional groups** and their reactivity. The **tautomeric equilibrium** can significantly influence the chemical properties of substances, affecting everything from their stability to their roles in biochemical processes.
Example of Keto and Enol Forms
A classic example of keto enol tautomerism is the interconversion between acetone and its enol form. While acetone predominantly exists in the keto form due to the stability provided by the carbonyl group, the enol form has its applications, particularly in reactions involving **nucleophiles** and **electrophiles**. Understanding these forms is also essential in areas like drug design, where the reactivity and interactions of **keto compounds** and **enol compounds** can influence therapeutic efficacy. Additionally, exploring reaction pathways provides insight into how molecular transformations occur during **chemical reactions**, further highlighting the relevance of keto enol tautomerism in organic synthesis.
The Role of Proton Transfer in Tautomerization
The transformation between keto and enol forms often involves proton transfer, an essential part of the **reaction mechanism**. When a **proton** shifts from the α-carbon to the carbonyl oxygen in the keto form, it results in the formation of the enol. This step can be favored by various **reaction conditions**, such as acidic or basic environments, which can either stabilize the keto or enol forms through **protonation** and **deprotonation** processes. Grasping this concept is vital for understanding the stability of these forms under specific conditions and their implications for **reaction kinetics**.
Keto-Enol Shifts and Their Significance
The significance of **keto-enol shifts** extends beyond simple chemical reactions; they play a role in
many biological processes as well. In the context of **biochemical reactions**, these shifts can affect **enzyme catalysis** and the overall rate of metabolic pathways. Because biological systems often rely on the precise balance between keto and enol forms, understanding the impact of these shifts provides critical insights into **biological relevance** and the functioning of biomolecules.
Stations of the Reaction and Their Energy States
The concept of **energy states** is crucial in visualizing keto-enol transitions. By mapping the potential energy of reactants and products, chemists can predict the direction of tautomerization and its favorability. The **equilibrium constant** associated with the tautomerization reaction indicates the extent to which equilibrium favors the keto or enol form. Thus, this energetics perspective is essential for synthetic strategies aiming to favor one form over another through controlled conditions like temperature or solvent selection.
Applications in Drug Design and Organic Synthesis
In pharmaceutical development, the implications of **keto enol tautomerism** are profound. The specific enantiomers of drugs can exhibit varied biological activities; thus, synthetic chemists pay close attention to their **reactivity patterns** and the effects of various substituents on the keto and enol forms during **organic synthesis**. For instance, medicinal chemists often need to consider the preferred tautomer of active compounds to optimize drug efficacy, which necessitates a clear understanding of their structural features and how the tautomerization influences their biological performance.
Impact of Solvents and Temperature on Tautomerization
The environment is deeply influential in the **tautomerization process**, with **solvent effects** being particularly notable. Depending on the solvent polarity and specific solvent-interaction with tautomeric forms, the equilibrium can shift significantly. Moreover, changing the **temperature** can alter the energy states of molecules, further impacting the tautomeric balance. Understanding how these variables interplay is crucial for chemists, as manipulating them allows for precise control over synthesis pathways in laboratory settings.
Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Tautomerization
The kinetics of keto enol tautomerism can vary widely depending on experimental conditions and the underlying **reaction mechanisms**. This aspect makes understanding reaction dynamics essential. Employing techniques from **analytical chemistry** to explore reaction rates provides insights about how fast a tautomerization event occurs and under what conditions. Furthermore, studies reveal how kinetic control can lead to one tautomer being favored over the other, thereby guiding synthetic strategies and the development of desired products in organic chemistry.
Optimal Conditions for Successful Tautomerization
Through careful experimentation, chemists can identify optimal conditions for tautomerization, including appropriate **pH levels**, temperature ranges, and solvent choices. By creating a controlled environment, researchers maximize the yield of either the keto or enol form and fine-tune the product selection in **substitution reactions**. Understanding this factor not only boosts efficiency in academia and industry but also aligns with the broader goals of organic synthesis towards enhanced chemical transformation.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
As we navigate the complexities of **keto enol tautomerism** in 2025, key insights emerge about its profound impact on **chemical transformations** and real-world applications. Emphasizing the significance of tautomeric equilibrium, the subtleties of hydrogen bonding, and the importance of various reaction conditions positions scientists to exploit these reactions in innovative ways.
- The relationship between keto and enol forms is foundational in organic chemistry.
- Enzymatic processes and drug design hinge on understanding tautomerization.
- Reaction conditions, including solvent and temperature, dramatically affect tautomeric outcomes.
- An comprehension of thermodynamics and kinetics related to tautomerization aids in optimizing synthetic strategies.
- Proper management of **proton transfer** mechanisms is pivotal in controlling reaction pathways.
FAQ
1. What is keto enol tautomerism?
Keto enol tautomerism refers to the chemical equilibrium between two isomeric forms: the keto form, which contains a carbonyl group, and the enol form, which features a hydroxyl group (−OH) attached to a double-bonded carbon. This interconversion is vital in organic reactions, allowing for the functional versatility of compounds.
2. How does solvent choice affect tautomerization?
The choice of solvent can significantly influence the stability of keto and enol forms. Polar solvents may stabilize the enol form, while nonpolar solvents often favor the keto form. Understanding these interactions is essential in manipulating **reaction conditions** to achieve desired outcomes in synthetic pathways.
3. What role does temperature play in keto enol tautomerism?
Temperature impacts the kinetic energy of molecules, thus affecting the rate and extent of tautomerization. Higher temperatures generally increase the reaction rate, leading to more favorable conditions for achieving tautomerization equilibrium, which can shift based on molecular interactions and the stability of the respective forms.
4. Why is tautomerization important in drug design?
Tautomerization is crucial in drug design because different tautomeric forms can exhibit varying biological activities. By understanding and controlling the tautomeric state, chemists can design more effective pharmaceuticals that are optimized for target interactions and biological pathways.
5. Can you explain the concept of tautomeric equilibrium?
Tautomeric equilibrium is the balance between the keto and enol forms of a compound, characterized by the equilibrium constant. This constant reflects how readily a compound converts from one form to another, which can vary depending on surrounding conditions such as pH, temperature, and solvent effects. Understanding this equilibrium is key to predicting chemical behavior.
6. How does acidity influence tautomerization?
The acidity of the environment can significantly impact tautomerization due to the role of proton transfer in the interconversion process. Acidic conditions can enhance the formation of the enol by facilitating protonation of intermediates, while basic conditions may stabilize the keto form. This relationship illustrates the importance of acid-base chemistry in steering tautomeric pathways.